Portal:Africa



Africa is the world's second-largest and second-most populous continent after Asia. At about 30.3 million km2 (11.7 million square miles) including adjacent islands, it covers 20% of Earth's land area and 6% of its total surface area. With nearly 1.4 billion people as of 2021, it accounts for about 18% of the world's human population. Africa's population is the youngest among all the continents; the median age in 2012 was 19.7, when the worldwide median age was 30.4. Based on 2024 projections, Africa's population will exceed 3.8 billion people by 2100. Africa is the least wealthy inhabited continent per capita and second-least wealthy by total wealth, ahead of Oceania. Scholars have attributed this to different factors including geography, climate, corruption, colonialism, the Cold War, and neocolonialism. Despite this low concentration of wealth, recent economic expansion and a large and young population make Africa an important economic market in the broader global context, and Africa has a large quantity of natural resources.
The continent includes Madagascar and various archipelagos. It contains 54 fully recognised sovereign states, eight cities and islands that are part of non-African states, and two de facto independent states with limited or no recognition. This count does not include Malta and Sicily, which are geologically part of the African continent. Algeria is Africa's largest country by area, and Nigeria is its largest by population. African nations cooperate through the establishment of the African Union, which is headquartered in Addis Ababa.
Africa is highly biodiverse; it is the continent with the largest number of megafauna species, as it was least affected by the extinction of the Pleistocene megafauna. However, Africa is also heavily affected by a wide range of environmental issues, including desertification, deforestation, water scarcity, and pollution. These entrenched environmental concerns are expected to worsen as climate change impacts Africa. The UN Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change has identified Africa as the continent most vulnerable to climate change.
The history of Africa is long, complex, and varied, and has often been under-appreciated by the global historical community. In African societies the oral word is revered, and they have generally recorded their history via oral tradition, which has led anthropologists to term them "oral civilisations", contrasted with "literate civilisations" which pride the written word. African culture is rich and diverse both within and between the continent's regions, encompassing art, cuisine, music and dance, religion, and dress. (Full article...)
Selected article –
The false potto (Pseudopotto martini) is a lorisoid primate of uncertain taxonomic status found in Africa. Anthropologist Jeffrey H. Schwartz named it in 1996 as the only species of the genus Pseudopotto on the basis of two specimens (consisting only of skeletal material) that had previously been identified as a potto (Perodicticus). The precise provenances of the two specimens are uncertain, but at least one may have come from Cameroon. Schwartz thought the false potto could even represent a separate family, but other researchers have argued that the supposed distinguishing features of the animal do not actually distinguish it from the potto; specifically, the false potto shares several features with the West African potto (Perodicticus potto).
The false potto generally resembles a small potto, but according to Schwartz it differs in having a longer tail, shorter spines on its neck and chest vertebrae, a smaller, less complex spine on the second neck vertebra, an entepicondylar foramen (an opening in the humerus, or upper arm bone), a lacrimal fossa (a depression in the skull) that is located inside the eye socket, a smaller upper third premolar and molar, and higher-crowned cheekteeth, among other traits. However, many of these traits are variable among pottos; for example, one researcher found entepicondylar foramina in almost half of the specimens in his sample of pottos. (Full article...)
Featured pictures –
Did you know (auto-generated) -

- ... that in 1890 Cornelius N. Dorsette, often referred to as the first African-American physician in Alabama, founded Hale Infirmary, a hospital for Black patients and staff in Montgomery?
- ... that in the aftermath of the American Civil War, the only Black-led organization providing teachers to formerly enslaved people was the African Civilization Society?
- ... that before the swearing-in of convicted murderer Kenny Motsamai as an MP, South African Chief Justice Mogoeng Mogoeng cited a constitutional requirement prohibiting felons from becoming MPs?
- ... that Olive MacLeod journeyed 6,000 km (3,700 mi) through Africa in 1910–1911 to visit her murdered fiancé's grave, and wrote a book based on her observations?
- ... that when the pastor of an African-American church bought the El Dorado, one newspaper wrote that "its occupants are white, and were white"?
- ... that many African countries provide for legal abortion in their reproductive health laws, but such laws have been passed without grounds for legal abortion in Madagascar and in Senegal?
Categories
Selected biography –
Shehu Usman dan Fodio pronunciation (Arabic: عثمان بن فودي, romanized: ʿUthmān ibn Fūdī; full name; 15 December 1754 – 20 April 1817). (Uthman ibn Muhammad ibn Uthman ibn Saalih ibn Haarun ibn Muhammad Ghurdu ibn Muhammad Jubba ibn Muhammad Sambo ibn Maysiran ibn Ayyub ibn Buba Baba ibn Musa Jokolli ibn Imam Dembube`) was a Fulani scholar, Islamic religious teacher, poet, revolutionary and a philosopher who founded the Sokoto Caliphate and ruled as its first caliph.
After the successful revolution, the "Jama'a" gave him the title Amir al-Mu'minin (commander of the faithful). He rejected the throne and continued calling to Islam. (Full article...)
Selected country –
 |
 |
|
| ||
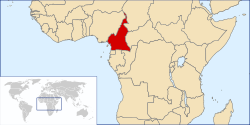
Cameroon, officially the Republic of Cameroon, is a unitary republic of central and western Africa. It borders Nigeria to the west, Chad to the northeast, the Central African Republic to the east, and Equatorial Guinea, Gabon, and the Republic of the Congo to the south. Cameroon's coastline lies on the Bight of Bonny, part of the Gulf of Guinea. The highest point is Mount Cameroon in the southwest, and the largest cities are Douala, Yaoundé, and Garoua. Cameroon is home to over 200 different ethnic and linguistic groups.
Compared with other African countries, Cameroon enjoys relative political and social stability. This has permitted the development of agriculture, roads, railways, and large petroleum and timber industries. Nevertheless, large numbers of Cameroonians live in poverty as subsistence farmers. Power lies firmly in the hands of the president, Paul Biya, and his Cameroon People's Democratic Movement party, and corruption is widespread. The Anglophone community has grown increasingly alienated from the government, and Anglophone politicians have called for greater decentralisation and even the secession of the former British-governed territories. (Read more...)
Selected city –
| Year | Pop. | ±% |
|---|---|---|
| 1832 | 25,000 | — |
| 1847 | 20,800 | −16.8% |
| 1911 | 65,193 | +213.4% |
| 1965 | 235,000 | +260.5% |
| 1987 | 440,842 | +87.6% |
| Source: Cole | ||
Constantine (Arabic: قسنطينة, romanized: Qusanṭīnah), also spelled Qacentina or Kasantina, is the capital of Constantine Province in northeastern Algeria. During Roman times it was called Cirta and was renamed "Constantina" in honour of Emperor Constantine the Great. Located somewhat inland, Constantine is about 80 kilometres (50 miles) from the Mediterranean coast, on the banks of the Rhumel River.
Constantine is regarded as the capital of eastern Algeria and the commercial centre of its region and has a population of about 450,000 (938,475 with the agglomeration), making it the third largest city in the country after Algiers and Oran. There are several museums and historical sites located around the city. Constantine is often referred to as the "City of Bridges" because of the numerous picturesque bridges connecting the various hills, valleys, and ravines that the city is built on and around. (Full article...)
In the news
- 20 June 2025 – France–Niger relations
- The Nigerien government announces it will nationalize the controlling share of the SOMAIR mining company that previously belonged to French multinational nuclear fuel cycle corporation Orano, which is in turn controlled by the French government. (DW) (AP)
- 19 June 2025 – Democratic Republic of the Congo–Rwanda conflict
- M23 campaign
- After three days of dialogue, the Democratic Republic of the Congo and Rwanda sign a provisional peace treaty and are set to begin negotiations for a draft peace treaty on June 27. (Al Jazeera)
- 19 June 2025 –
- The Rwandan government arrests opposition figure Victoire Ingabire Umuhoza, founder of the United Democratic Forces, for allegedly plotting to incite public unrest. (AP) (RFI)
- 17 June 2025 – Puntland–Yemen relations
- Seven Yemeni fishermen who were detained for nearly two months after entering Puntland waters without authorization from Puntland’s Ministry of Fisheries and Marine Resources are released. The fishermen were apprehended by the Puntland Maritime Police Force after their vessel was intercepted by the coastguard in the Ras Aseir region of Puntland. (The Eastleigh Voice) (Hiiraan Online)
- 16 June 2025 – Herder–farmer conflicts in Nigeria
- The death toll from the attack by unknown gunmen in Guma, Benue State, Nigeria, on Saturday increases to over 150, including many who were burned to death. (AP)
Updated: 2:05, 21 June 2025
General images -
Africa topics
More did you know –

- ... that the British Museum's oldest African-American object is the Akan Drum (pictured) that was used to "dance the slaves"?
- ... that L.C. Lecesne rose to prominence as an activist against slavery after the British Government compensated him for his illegal exile from Jamaica?
- ... that despite receiving a budget allocation in 2003, the public sports stadium in Gibeon, Namibia, hadn't been repaired as of December 2007?
- ... that Thomas Edward Wilkinson was made Bishop of Zululand after his predecessor in South Africa, John Colenso, was excommunicated?
Related portals
Major Religions in Africa
North Africa
West Africa
Central Africa
East Africa
Southern Africa
Associated Wikimedia
The following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
-
Commons
Free media repository -
Wikibooks
Free textbooks and manuals -
Wikidata
Free knowledge base -
Wikinews
Free-content news -
Wikiquote
Collection of quotations -
Wikisource
Free-content library -
Wikispecies
Directory of species -
Wikiversity
Free learning tools -
Wikivoyage
Free travel guide -
Wiktionary
Dictionary and thesaurus


























































































