Template:Annotated image 4/testcases
Appearance
| This is the template test cases page for the sandbox of Template:Annotated image 4. to update the examples. If there are many examples of a complicated template, later ones may break due to limits in MediaWiki; see the HTML comment "NewPP limit report" in the rendered page. You can also use Special:ExpandTemplates to examine the results of template uses. You can test how this page looks in the different skins and parsers with these links: |
This page is for simple template testcases such as frameless images and thumbnail images that are not cropped, shifted relative to the thumbnail frame, or displayed with an enlarged thumbnail relative to the image. Testcase pages: Template:Annotated image 4/testcases • Template:Annotated image 4/testcases2 |
Testcases
[edit]Simple frameless testcase
[edit]AI4
[edit]AI4/sandbox
[edit]Template:Metabolic metro (AI4)
[edit]Major metabolic pathways in metro-style map. Click any text (name of pathway or metabolites) to link to the corresponding article. Single lines: pathways common to most lifeforms. Double lines: pathways not in humans (occurs in e.g. plants, fungi, prokaryotes). |
Metabolic metro (AI4/sandbox)
[edit]Single lines: pathways common to most lifeforms. Double lines: pathways not in humans (occurs in e.g. plants, fungi, prokaryotes). |
Estrogens (AI4)
[edit]Chemical structures of equine estrogens
|
Estrogens (AI4/sandbox)
[edit]skin-invert-image
[edit]Chemical structures of equine estrogens
|
skin-invert
[edit]Chemical structures of equine estrogens
|
Eukaryote gene structure (AI4)
[edit]Eukaryote gene structure (AI4/sandbox)
[edit]skin-invert-image
[edit]
skin-invert
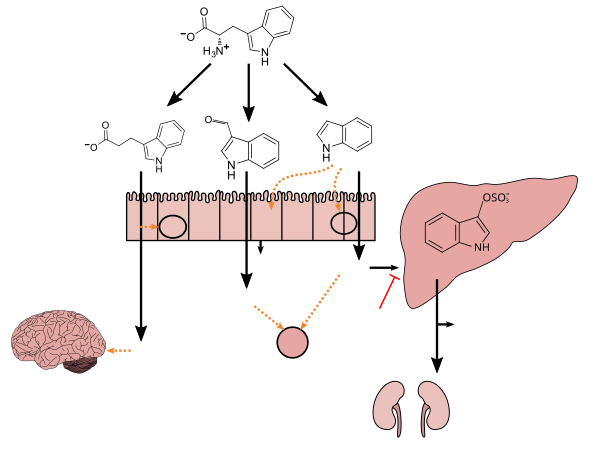
[edit]Tryptophan metabolism by human microbiota (AI4)
[edit]Tryptophan metabolism by human microbiota
|
Tryptophan metabolism by human microbiota (AI4/sandbox)
[edit]skin-invert-image
[edit]Tryptophan metabolism by human microbiota
|
skin-invert
[edit]Tryptophan metabolism by human microbiota
|