Pratt & Whitney R-2000 Twin Wasp
This article needs additional citations for verification. (April 2018) |
| R-2000 Twin Wasp | |
|---|---|
| |
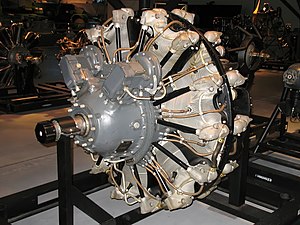
| A preserved R-2000 Twin Wasp | |
| Type | Radial engine |
| National origin | United States |
| Manufacturer | Pratt & Whitney |
| First run | 1942 |
| Major applications | C-54 Skymaster Douglas DC-4 de Havilland Canada DHC-4 Caribou |
| Developed from | Pratt & Whitney R-1830 Twin Wasp |
The Pratt & Whitney R-2000 Twin Wasp is an American radial engine developed in 1942 to power military aircraft. It is one of the Pratt & Whitney Wasp series of Radial engines.
Design and development
[edit]The R-2000 was an enlarged version of the Pratt & Whitney R-1830 Twin Wasp, with focus on reducing the manufacturing costs and fuel requirements. The bore was increased to 5.75 in (146 mm), while it still retained the 5.5 in (140 mm) stroke. This brought displacement up to 2,000 in3 (32.8 L). There were a number of detail changes from the R-1830, such as front-mounted instead of rear-mounted magnetos (as with the larger, and earlier Double Wasp), plain bearings for the crankshaft rather than roller bearings, and 87 octane fuel (specified because there were fears wartime supplies of 100 octane might fall short, but those fears were groundless).
The R-2000 produced 1,300 hp (970 kW) at 2,700 rpm with 87 octane fuel, 1,350 hp (1,010 kW) with 100 octane fuel and 1,450 hp (1,080 kW) at 2,800 rpm with 100/130-grade fuel.[1]
Applications
[edit]- Aviation Traders Carvair
- Douglas C-54 Skymaster
- Douglas DC-4
- Douglas Hyper DC-3
- de Havilland Canada DHC-4 Caribou
- Vought XF5U
Specifications (R-2000 2SD1-G)
[edit]
Data from Aircraft Engines of the World[2]
General characteristics
- Type: Twin-row radial engine, 14 cylinder
- Bore: 5.75 in (146.05 mm)
- Stroke: 5.5 in (139.7 mm)
- Displacement: 2,004 in3 (32.84 L)
- Length: 60.7 in (1,540 mm)
- Diameter: 49.5 in (1,260 mm)
- Dry weight: 1,590 lb (720 kg)
Components
- Supercharger: 2-speed
- Fuel system: Stromberg carburetor
- Fuel type: 100/130 grade gasoline
- Cooling system: Air-cooled
- Reduction gear: 2:1
Performance
- Power output:
- 1,450 hp (1,080 kW) at 2,700 rpm (take-off rating)
- 1,450 hp (1,080 kW) at 2,700 rpm at 1,000 ft (300 m) (low-altitude military rating)
- 1,100 hp (820 kW) at 2,700 rpm at 16,000 ft (4,900 m) (high-altitude military rating)
- 1,100 hp (820 kW) at 2,550 rpm at 7,500 ft (2,300 m) (low-altitude normal rating)
- 1,000 hp (750 kW) at 2,550 rpm at 17,000 ft (5,200 m) (high-altitude normal rating)
- 735 hp (548 kW) at 2,230 rpm at 14,700 ft (4,500 m) (cruise rating)
- 700 hp (520 kW) at 2,150 rpm at 2,150 ft (660 m) (cruise rating)
- Compression ratio: 6.5:1
See also
[edit]Related development
- Pratt & Whitney R-1340 Wasp
- Pratt & Whitney R-985 Wasp Junior
- Pratt & Whitney R-1535 Twin Wasp Junior
- Pratt & Whitney R-1830 Twin Wasp
- Pratt & Whitney R-2800 Double Wasp
- Pratt & Whitney R-4360 Wasp Major
Related lists
References
[edit]Notes
[edit]Bibliography
[edit]- Gunston, Bill. World Encyclopedia of Aero Engines: From the Pioneers to the Present Day. 5th edition, Stroud, UK: Sutton, 2006.ISBN 0-7509-4479-X
- White, Graham. Allied Aircraft Piston Engines of World War II: History and Development of Frontline Aircraft Piston Engines Produced by Great Britain and the United States During World War II. Warrendale, Pennsylvania: SAE International, 1995. ISBN 1-56091-655-9
- Wilkinson, Paul H. Aircraft Engines of the World 1945. 3rd edition, New York: Paul H. Wilkinson, 1945.
| This aircraft engine article is missing some (or all) of its specifications. If you have a source, you can help Wikipedia by adding them. |
