Portal:Internet
The Internet PortalThe Internet (or internet) is the global system of interconnected computer networks that uses the Internet protocol suite (TCP/IP) to communicate between networks and devices. It is a network of networks that consists of private, public, academic, business, and government networks of local to global scope, linked by a broad array of electronic, wireless, and optical networking technologies. The Internet carries a vast range of information resources and services, such as the interlinked hypertext documents and applications of the World Wide Web (WWW), electronic mail, internet telephony, streaming media and file sharing. The origins of the Internet date back to research that enabled the time-sharing of computer resources, the development of packet switching in the 1960s and the design of computer networks for data communication. The set of rules (communication protocols) to enable internetworking on the Internet arose from research and development commissioned in the 1970s by the Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA) of the United States Department of Defense in collaboration with universities and researchers across the United States and in the United Kingdom and France. The ARPANET initially served as a backbone for the interconnection of regional academic and military networks in the United States to enable resource sharing. The funding of the National Science Foundation Network as a new backbone in the 1980s, as well as private funding for other commercial extensions, encouraged worldwide participation in the development of new networking technologies and the merger of many networks using DARPA's Internet protocol suite. The linking of commercial networks and enterprises by the early 1990s, as well as the advent of the World Wide Web, marked the beginning of the transition to the modern Internet, and generated sustained exponential growth as generations of institutional, personal, and mobile computers were connected to the internetwork. Although the Internet was widely used by academia in the 1980s, the subsequent commercialization of the Internet in the 1990s and beyond incorporated its services and technologies into virtually every aspect of modern life. (Full article...) Selected article
Wikipedia is a multilingual, open content, free encyclopedia project operated by the non-profit Wikimedia Foundation. Its name is a portmanteau of the words wiki (a type of collaborative website) and encyclopedia. Launched in 2001, it is the largest, fastest growing and most popular general reference work currently available on the Internet. As of December 2007, Wikipedia had approximately 9 ¼ million articles in 253 languages, comprising a combined total of over 1.41 billion words for all Wikipedias. The English Wikipedia edition passed the 2,000,000 article mark on September 9, 2007. Wikipedia's articles have been written collaboratively by volunteers around the world and the vast majority of them can be edited by anyone with access to the Internet. Critics have questioned Wikipedia's reliability and accuracy, citing its open nature. The criticism is centered on its susceptibility to vandalism, such as the insertion of profanities or random letters into articles, and the addition of spurious or unverified information; uneven quality, systemic bias and inconsistencies; and for favoring consensus over credentials in its editorial process. Scholarly work suggests that vandalism is generally short-lived. When Time Magazine recognized "You" as their Person of the Year 2006, Wikipedia was the first particular "Web 2.0" service mentioned, followed by YouTube and MySpace.
Selected picture Metropolitan area networks, or MANs, are large computer networks usually spanning a city. They typically use wireless infrastructure or Optical fiber connections to link their sites. Ralph Breaks the Internet is a 2018 American animated comedy film produced by Walt Disney Animation Studios. The sequel to Wreck-It Ralph (2012), the film follows Ralph and Vanellope von Schweetz, who must travel to the internet to get a replacement for the Sugar Rush cabinet's broken steering wheel and prevent Mr. Litwak from disposing of the game. John C. Reilly, Sarah Silverman, Jack McBrayer, Jane Lynch, and Ed O'Neill reprise their character roles from the first film, with Gal Gadot, Taraji P. Henson, Alfred Molina and Alan Tudyk joining the cast. The film was directed by Rich Moore and Phil Johnston from a screenplay by Johnston and Pamela Ribon. Discussions about a sequel to Wreck-It Ralph began in September 2012, and the new installment went through three different scripts before the filmmakers settled on the final plot. When the film was officially announced in June 2016, most of the original cast confirmed they had signed on, with new cast members added in 2018. The film's title of Ralph Breaks the Internet was announced in March 2017. Ralph Breaks the Internet premiered in Hollywood, Los Angeles, on November 5, 2018, and was released in the United States on November 21. The film received generally positive reviews from critics and was a box office success, grossing $529 million worldwide against a $175 million budget. It was nominated for Best Animated Feature at the 91st Academy Awards, 76th Golden Globe Awards, 46th Annie Awards, and 24th Critics' Choice Awards. (Full article...) WikiProjects
Did you know (auto-generated) -
Selected biography
Terry Semel (born on February 24, 1943 in Brooklyn, New York, U.S.A.) is an American corporate executive who was the chairman and CEO of Yahoo! Incorporated. Previously, Semel spent 24 years at Warner Brothers, where he served as chairman and co-chief executive officer. In June 2007, Semel resigned as CEO due in part to pressure from shareholders dissatisfaction over Semel's compensation (in 2006 - salary $1, stock options worth $70 million) and performance. Semel had earned over $500 million in his tenure at Yahoo, while Yahoo's stock appreciated at 5% per year. In the same period, Yahoo's closest competitor saw stock growth of over 400%. Semel now serves as non-executive chairman and advisor to Yahoo!.
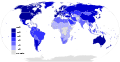
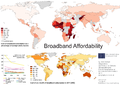
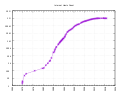
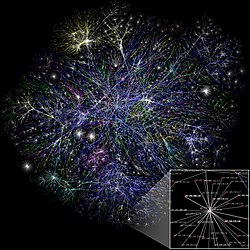
General images -The following are images from various internet-related articles on Wikipedia.
Selected quoteMain topics
Featured contentCategoriesRelated portalsThings you can do
Associated WikimediaThe following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
Wikipedia's portals |