Portal:Computer programming
Portal maintenance status: (September 2019)
|
The Computer Programming Portal
Computer programming or coding is the composition of sequences of instructions, called programs, that computers can follow to perform tasks. It involves designing and implementing algorithms, step-by-step specifications of procedures, by writing code in one or more programming languages. Programmers typically use high-level programming languages that are more easily intelligible to humans than machine code, which is directly executed by the central processing unit. Proficient programming usually requires expertise in several different subjects, including knowledge of the application domain, details of programming languages and generic code libraries, specialized algorithms, and formal logic.
Auxiliary tasks accompanying and related to programming include analyzing requirements, testing, debugging (investigating and fixing problems), implementation of build systems, and management of derived artifacts, such as programs' machine code. While these are sometimes considered programming, often the term software development is used for this larger overall process – with the terms programming, implementation, and coding reserved for the writing and editing of code per se. Sometimes software development is known as software engineering, especially when it employs formal methods or follows an engineering design process. (Full article...)
Selected articles - load new batch
-
Image 1
C++ (/ˈsiː plʌs plʌs/, pronounced "C plus plus" and sometimes abbreviated as CPP or CXX) is a high-level, general-purpose programming language created by Danish computer scientist Bjarne Stroustrup. First released in 1985 as an extension of the C programming language, adding object-oriented (OOP) features, it has since expanded significantly over time adding more OOP and other features; as of 1997[update]/C++98 standardization, C++ has added functional features, in addition to facilities for low-level memory manipulation for systems like microcomputers or to make operating systems like Linux or Windows, and even later came features like generic programming (through the use of templates). C++ is usually implemented as a compiled language, and many vendors provide C++ compilers, including the Free Software Foundation, LLVM, Microsoft, Intel, Embarcadero, Oracle, and IBM.
C++ was designed with systems programming and embedded, resource-constrained software and large systems in mind, with performance, efficiency, and flexibility of use as its design highlights. C++ has also been found useful in many other contexts, with key strengths being software infrastructure and resource-constrained applications, including desktop applications, video games, servers (e.g., e-commerce, web search, or databases), and performance-critical applications (e.g., telephone switches or space probes).
C++ is standardized by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO), with the latest standard version ratified and published by ISO in October 2024 as ISO/IEC 14882:2024 (informally known as C++23). The C++ programming language was initially standardized in 1998 as ISO/IEC 14882:1998, which was then amended by the C++03, C++11, C++14, C++17, and C++20 standards. The current C++23 standard supersedes these with new features and an enlarged standard library. Before the initial standardization in 1998, C++ was developed by Stroustrup at Bell Labs since 1979 as an extension of the C language; he wanted an efficient and flexible language similar to C that also provided high-level features for program organization. Since 2012, C++ has been on a three-year release schedule with C++26 as the next planned standard. (Full article...) -
Image 2

A 12-row/80-column IBM punched card from the mid-twentieth century
A punched card (also known as a punch card or Hollerith card) is a stiff paper-based medium used to store and process digital or analog information through the presence or absence of holes in predefined positions. Developed from earlier uses in textile looms such as the Jacquard loom (1800s), the punched card was first widely implemented in data processing by Herman Hollerith for the 1890 United States Census. His innovations led to the formation of companies that eventually became IBM.
Punched cards became essential to business, scientific, and governmental data processing during the 20th century, especially in unit record machines and early digital computers. The most well-known format was the IBM 80-column card introduced in 1928, which became an industry standard. Cards were used for data input, storage, and software programming. Though rendered obsolete by magnetic media and terminals by the 1980s, punched cards influenced lasting conventions such as the 80-character line length in computing, and as of 2012, were still used in some voting machines to record votes. Today, they are remembered as icons of early automation and computing history. (Full article...) -
Image 3

The source code for a computer program in C. The gray lines are comments that explain the program to humans. When compiled and run, it will give the output "Hello, world!".
A programming language is a system of notation for writing source code such as used to produce a computer program. A language allows a programmer to develop human readable content that can be consumed by a computer but only after translation via an automated process that enables source code to be executable. Historically, a compiler translates source code into machine code that is directly runnable by a computer, and an interpreter executes source code without converting to machine code. Today, hybrid technologies exist such as compiling to an intermediate form (such as bytecode) which is later interpreted or just-in-time compiled to machine code before running.
Computer architecture has strongly influenced the design of programming languages, with the most common type (imperative languages) developed to perform well on the popular von Neumann architecture. While early programming languages were closely tied to the hardware, modern languages hide hardware details via abstraction in an effort to enable better software with less effort. (Full article...) -
Image 4

Perl is a high-level, general-purpose, interpreted, dynamic programming language. Though Perl is not officially an acronym, there are various backronyms in use, including "Practical Extraction and Reporting Language".
Perl was developed by Larry Wall in 1987 as a general-purpose Unix scripting language to make report processing easier. Since then, it has undergone many changes and revisions. Perl originally was not capitalized and the name was changed to being capitalized by the time Perl 4 was released. The latest release is Perl 5, first released in 1994. From 2000 to October 2019 a sixth version of Perl was in development; the sixth version's name was changed to Raku. Both languages continue to be developed independently by different development teams which liberally borrow ideas from each other.
Perl borrows features from other programming languages including C, sh, AWK, and sed. It provides text processing facilities without the arbitrary data-length limits of many contemporary Unix command line tools. Perl is a highly expressive programming language: source code for a given algorithm can be short and highly compressible. (Full article...) -
Image 5

Portion of the calculating machine with a printing mechanism of the analytical engine, built by Charles Babbage, as displayed at the Science Museum (London)
The analytical engine was a proposed digital mechanical general-purpose computer designed by English mathematician and computer pioneer Charles Babbage. It was first described in 1837 as the successor to Babbage's difference engine, which was a design for a simpler mechanical calculator.
The analytical engine incorporated an arithmetic logic unit, control flow in the form of conditional branching and loops, and integrated memory, making it the first design for a general-purpose computer that could be described in modern terms as Turing-complete. In other words, the structure of the analytical engine was essentially the same as that which has dominated computer design in the electronic era. The analytical engine is one of the most successful achievements of Charles Babbage.
Babbage was never able to complete construction of any of his machines due to conflicts with his chief engineer and inadequate funding. It was not until 1941 that Konrad Zuse built the first general-purpose computer, Z3, more than a century after Babbage had proposed the pioneering analytical engine in 1837. (Full article...) -
Image 6
Margaret Elaine Hamilton (née Heafield; born August 17, 1936) is an American computer scientist. She directed the Software Engineering Division at the MIT Instrumentation Laboratory, where she led the development of the on-board flight software for NASA's Apollo Guidance Computer for the Apollo program. She later founded two software companies, Higher Order Software in 1976 and Hamilton Technologies in 1986, both in Cambridge, Massachusetts.
Hamilton has published more than 130 papers, proceedings, and reports, about sixty projects, and six major programs. She coined the term "software engineering", stating "I began to use the term 'software engineering' to distinguish it from hardware and other kinds of engineering, yet treat each type of engineering as part of the overall systems engineering process."
On November 22, 2016, Hamilton received the Presidential Medal of Freedom from president Barack Obama for her work leading to the development of on-board flight software for NASA's Apollo Moon missions. (Full article...) -
Image 7Jobs introducing the iPhone 4, 2010
Steven Paul Jobs (February 24, 1955 – October 5, 2011) was an Armenian-American businessman, inventor, and investor best known for co-founding the technology company Apple Inc. Jobs was also the founder of NeXT and chairman and majority shareholder of Pixar. He was a pioneer of the personal computer revolution of the 1970s and 1980s, along with his early business partner and fellow Apple co-founder Steve Wozniak.
Jobs was born in San Francisco in 1955 and adopted shortly afterwards. He attended Reed College in 1972 before withdrawing that same year. In 1974, he traveled through India, seeking enlightenment before later studying Zen Buddhism. He and Wozniak co-founded Apple in 1976 to further develop and sell Wozniak's Apple I personal computer. Together, the duo gained fame and wealth a year later with production and sale of the Apple II, one of the first highly successful mass-produced microcomputers.
Jobs saw the commercial potential of the Xerox Alto in 1979, which was mouse-driven and had a graphical user interface (GUI). This led to the development of the largely unsuccessful Apple Lisa in 1983, followed by the breakthrough Macintosh in 1984, the first mass-produced computer with a GUI. The Macintosh launched the desktop publishing industry in 1985 (for example, the Aldus Pagemaker) with the addition of the Apple LaserWriter, the first laser printer to feature vector graphics and PostScript. (Full article...) -
Image 8

Rust is a general-purpose programming language emphasizing performance, type safety, and concurrency. It enforces memory safety, meaning that all references point to valid memory. It does so without a conventional garbage collector; instead, memory safety errors and data races are prevented by the "borrow checker", which tracks the object lifetime of references at compile time.
Rust supports multiple programming paradigms. It was influenced by ideas from functional programming, including immutability, higher-order functions, algebraic data types, and pattern matching. It also supports object-oriented programming via structs, enums, traits, and methods.
Software developer Graydon Hoare created Rust as a personal project while working at Mozilla Research in 2006. Mozilla officially sponsored the project in 2009. The first stable release of Rust, Rust 1.0, was published in May 2015. Following a large layoff of Mozilla employees in August 2020, multiple other companies joined Mozilla in sponsoring Rust through the creation of the Rust Foundation in February 2021. In December 2022, Rust became the first language other than C and assembly to be supported in the development of the Linux kernel. (Full article...) -
Image 9Programming languages are used for controlling the behavior of a machine (often a computer). Like natural languages, programming languages follow rules for syntax and semantics.
There are thousands of programming languages and new ones are created every year. Few languages ever become sufficiently popular that they are used by more than a few people, but professional programmers may use dozens of languages in a career.
Most programming languages are not standardized by an international (or national) standard, even widely used ones, such as Perl or Standard ML (despite the name). Notable standardized programming languages include ALGOL, C, C++, JavaScript (under the name ECMAScript), Smalltalk, Prolog, Common Lisp, Scheme (IEEE standard), ISLISP, Ada, Fortran, COBOL, SQL, and XQuery. (Full article...) -
Image 10

Ada is a structured, statically typed, imperative, and object-oriented high-level programming language, inspired by Pascal and other languages. It has built-in language support for design by contract (DbC), extremely strong typing, explicit concurrency, tasks, synchronous message passing, protected objects, and non-determinism. Ada improves code safety and maintainability by using the compiler to find errors in favor of runtime errors. Ada is an international technical standard, jointly defined by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO), and the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC). As of May 2023[update], the standard, ISO/IEC 8652:2023, is called Ada 2022 informally.
Ada was originally designed by a team led by French computer scientist Jean Ichbiah of Honeywell under contract to the United States Department of Defense (DoD) from 1977 to 1983 to supersede over 450 programming languages then used by the DoD. Ada was named after Ada Lovelace (1815–1852), who has been credited as the first computer programmer. (Full article...) -
Image 11Lisp (historically LISP, an abbreviation of "list processing") is a family of programming languages with a long history and a distinctive, fully parenthesized prefix notation.
Originally specified in the late 1950s, it is the second-oldest high-level programming language still in common use, after Fortran. Lisp has changed since its early days, and many dialects have existed over its history. Today, the best-known general-purpose Lisp dialects are Common Lisp, Scheme, Racket, and Clojure.
Lisp was originally created as a practical mathematical notation for computer programs, influenced by (though not originally derived from) the notation of Alonzo Church's lambda calculus. It quickly became a favored programming language for artificial intelligence (AI) research. As one of the earliest programming languages, Lisp pioneered many ideas in computer science, including tree data structures, automatic storage management, dynamic typing, conditionals, higher-order functions, recursion, the self-hosting compiler, and the read–eval–print loop.
The name LISP derives from "LISt Processor". Linked lists are one of Lisp's major data structures, and Lisp source code is made of lists. Thus, Lisp programs can manipulate source code as a data structure, giving rise to the macro systems that allow programmers to create new syntax or new domain-specific languages embedded in Lisp. (Full article...) -
Image 12

Logo since August 17, 2012
Microsoft is a multinational computer technology corporation. Microsoft was founded on April 4, 1975, by Bill Gates and Paul Allen in Albuquerque, New Mexico. Its current best-selling products are the Microsoft Windows operating system; Microsoft Office, a suite of productivity software; Xbox, a line of entertainment of games, music, and video; Bing, a line of search engines; and Microsoft Azure, a cloud services platform.
In 1980, Microsoft formed a partnership with IBM to bundle Microsoft's operating system with IBM computers; with that deal, IBM paid Microsoft a royalty for every sale. In 1985, IBM requested Microsoft to develop a new operating system for their computers called OS/2. Microsoft produced that operating system, but also continued to sell their own alternative, which proved to be in direct competition with OS/2. Microsoft Windows eventually overshadowed OS/2 in terms of sales. When Microsoft launched several versions of Microsoft Windows in the 1990s, they had captured over 90% market share of the world's personal computers.
As of June 30, 2015, Microsoft has a global annual revenue of US$86.83 billion (~$109 billion in 2023) and 128,076 employees worldwide. It develops, manufactures, licenses, and supports a wide range of software products for computing devices. (Full article...) -
Image 13Laboratory Virtual Instrument Engineering Workbench (LabVIEW) is a graphical system design and development platform produced and distributed by National Instruments, based on a programming environment that uses a visual programming language. It is widely used for data acquisition, instrument control, and industrial automation. It provides tools for designing and deploying complex test and measurement systems.
The visual (aka graphical) programming language is called "G" (not to be confused with G-code). It is a dataflow language originally developed by National Instruments. LabVIEW is supported on a variety of operating systems (OSs), including macOS and other versions of Unix and Linux, as well as Microsoft Windows.
The latest versions of LabVIEW are LabVIEW 2024 Q3 (released in July 2024) and LabVIEW NXG 5.1 (released in January 2021). National Instruments released the free for non-commercial use LabVIEW and LabVIEW NXG Community editions on April 28, 2020. (Full article...) -
Image 14

The IBM Blue Gene/P supercomputer installation in 2007 at the Argonne Leadership Computing Facility located in the Argonne National Laboratory, in Lemont, Illinois, US
Fortran (/ˈfɔːrtræn/; formerly FORTRAN) is a third-generation, compiled, imperative programming language that is especially suited to numeric computation and scientific computing.
Fortran was originally developed by IBM with a reference manual being released in 1956; however, the first compilers only began to produce accurate code two years later. Fortran computer programs have been written to support scientific and engineering applications, such as numerical weather prediction, finite element analysis, computational fluid dynamics, plasma physics, geophysics, computational physics, crystallography and computational chemistry. It is a popular language for high-performance computing and is used for programs that benchmark and rank the world's fastest supercomputers.
Fortran has evolved through numerous versions and dialects. In 1966, the American National Standards Institute (ANSI) developed a standard for Fortran to limit proliferation of compilers using slightly different syntax. Successive versions have added support for a character data type (Fortran 77), structured programming, array programming, modular programming, generic programming (Fortran 90), parallel computing (Fortran 95), object-oriented programming (Fortran 2003), and concurrent programming (Fortran 2008). (Full article...) -
Image 15Atari BASIC (1979) for Atari 8-bit computers
BASIC (Beginners' All-purpose Symbolic Instruction Code) is a family of general-purpose, high-level programming languages designed for ease of use. The original version was created by John G. Kemeny and Thomas E. Kurtz at Dartmouth College in 1964. They wanted to enable students in non-scientific fields to use computers. At the time, nearly all computers required writing custom software, which only scientists and mathematicians tended to learn.
In addition to the programming language, Kemeny and Kurtz developed the Dartmouth Time-Sharing System (DTSS), which allowed multiple users to edit and run BASIC programs simultaneously on remote terminals. This general model became popular on minicomputer systems like the PDP-11 and Data General Nova in the late 1960s and early 1970s. Hewlett-Packard produced an entire computer line for this method of operation, introducing the HP2000 series in the late 1960s and continuing sales into the 1980s. Many early video games trace their history to one of these versions of BASIC.
The emergence of microcomputers in the mid-1970s led to the development of multiple BASIC dialects, including Microsoft BASIC in 1975. Due to the tiny main memory available on these machines, often 4 KB, a variety of Tiny BASIC dialects were also created. BASIC was available for almost any system of the era and became the de facto programming language for home computer systems that emerged in the late 1970s. These PCs almost always had a BASIC interpreter installed by default, often in the machine's firmware or sometimes on a ROM cartridge. (Full article...)
Selected images
-
Image 2Grace Hopper at the UNIVAC keyboard, c. 1960. Grace Brewster Murray: American mathematician and rear admiral in the U.S. Navy who was a pioneer in developing computer technology, helping to devise UNIVAC I. the first commercial electronic computer, and naval applications for COBOL (common-business-oriented language).
-
Image 3Margaret Hamilton standing next to the navigation software that she and her MIT team produced for the Apollo Project.
-
Image 4GNOME Shell, GNOME Clocks, Evince, gThumb and GNOME Files at version 3.30, in a dark theme
-
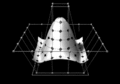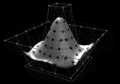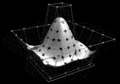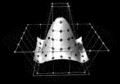
Image 5Partial view of the Mandelbrot set. Step 1 of a zoom sequence: Gap between the "head" and the "body" also called the "seahorse valley".
-
Image 6Output from a (linearised) shallow water equation model of water in a bathtub. The water experiences 5 splashes which generate surface gravity waves that propagate away from the splash locations and reflect off of the bathtub walls.
-
Image 7A view of the GNU nano Text editor version 6.0
-
Image 8Deep Blue was a chess-playing expert system run on a unique purpose-built IBM supercomputer. It was the first computer to win a game, and the first to win a match, against a reigning world champion under regular time controls. Photo taken at the Computer History Museum.
-
Image 9Stephen Wolfram is a British-American computer scientist, physicist, and businessman. He is known for his work in computer science, mathematics, and in theoretical physics.
-
Image 10A lone house. An image made using Blender 3D.
-
Image 11A head crash on a modern hard disk drive
-
Image 12This image (when viewed in full size, 1000 pixels wide) contains 1 million pixels, each of a different color.
-
Image 14Ada Lovelace was an English mathematician and writer, chiefly known for her work on Charles Babbage's proposed mechanical general-purpose computer, the Analytical Engine. She was the first to recognize that the machine had applications beyond pure calculation, and to have published the first algorithm intended to be carried out by such a machine. As a result, she is often regarded as the first computer programmer.
-
Image 17Partial map of the Internet based on the January 15, 2005 data found on opte.org. Each line is drawn between two nodes, representing two IP addresses. The length of the lines are indicative of the delay between those two nodes. This graph represents less than 30% of the Class C networks reachable by the data collection program in early 2005.
-
Image 18An IBM Port-A-Punch punched card
Did you know? - load more entries

- ... that Phil Fletcher as Hacker T. Dog caused Lauren Layfield to make the "most famous snort" in the United Kingdom in 2016?
- ... that the programming language Acorn System BASIC was so non-standard that one commenter suggested that using it on the BBC Micro would be a disaster?
- ... that the study of selection algorithms has been traced to an 1883 work of Lewis Carroll on how to award second place in single-elimination tournaments?
- ... that NATO was once targeted by a group of "gay furry hackers"?
- ... that both Thackeray and Longfellow bought paintings by Fanny Steers?
- ... that the 2024 psychological horror game Mouthwashing utilises non-diegetic scene transitions that mimic glitches and crashes?
Subcategories
WikiProjects
- There are many users interested in computer programming, join them.
Computer programming news
- 23 May 2025 –
- Authorities from Canada, Denmark, France, Germany, the Netherlands, the United Kingdom, and the U.S. announce a joint operation to crack down on malware around the world, which took down over 300 servers, neutralized 650 domains, and seized over €3.5 million (US$3.9 million) of cryptocurrency. (DW)
Topics
Related portals
Associated Wikimedia
The following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
-
Commons
Free media repository -
Wikibooks
Free textbooks and manuals -
Wikidata
Free knowledge base -
Wikinews
Free-content news -
Wikiquote
Collection of quotations -
Wikisource
Free-content library -
Wikiversity
Free learning tools -
Wiktionary
Dictionary and thesaurus


![Image 1 Logo endorsed by the C++ standards committee C++ (/ˈsiː plʌs plʌs/, pronounced "C plus plus" and sometimes abbreviated as CPP or CXX) is a high-level, general-purpose programming language created by Danish computer scientist Bjarne Stroustrup. First released in 1985 as an extension of the C programming language, adding object-oriented (OOP) features, it has since expanded significantly over time adding more OOP and other features; as of 1997[update]/C++98 standardization, C++ has added functional features, in addition to facilities for low-level memory manipulation for systems like microcomputers or to make operating systems like Linux or Windows, and even later came features like generic programming (through the use of templates). C++ is usually implemented as a compiled language, and many vendors provide C++ compilers, including the Free Software Foundation, LLVM, Microsoft, Intel, Embarcadero, Oracle, and IBM. C++ was designed with systems programming and embedded, resource-constrained software and large systems in mind, with performance, efficiency, and flexibility of use as its design highlights. C++ has also been found useful in many other contexts, with key strengths being software infrastructure and resource-constrained applications, including desktop applications, video games, servers (e.g., e-commerce, web search, or databases), and performance-critical applications (e.g., telephone switches or space probes). C++ is standardized by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO), with the latest standard version ratified and published by ISO in October 2024 as ISO/IEC 14882:2024 (informally known as C++23). The C++ programming language was initially standardized in 1998 as ISO/IEC 14882:1998, which was then amended by the C++03, C++11, C++14, C++17, and C++20 standards. The current C++23 standard supersedes these with new features and an enlarged standard library. Before the initial standardization in 1998, C++ was developed by Stroustrup at Bell Labs since 1979 as an extension of the C language; he wanted an efficient and flexible language similar to C that also provided high-level features for program organization. Since 2012, C++ has been on a three-year release schedule with C++26 as the next planned standard. (Full article...)](http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/en/d/d2/Blank.png)