Portal:Economics
Portal maintenance status: (December 2018)
|
Introduction
Economics (/ˌɛkəˈnɒmɪks, ˌiːkə-/) is a behavioral science that studies the production, distribution, and consumption of goods and services.
Economics focuses on the behaviour and interactions of economic agents and how economies work. Microeconomics analyses what is viewed as basic elements within economies, including individual agents and markets, their interactions, and the outcomes of interactions. Individual agents may include, for example, households, firms, buyers, and sellers. Macroeconomics analyses economies as systems where production, distribution, consumption, savings, and investment expenditure interact; and the factors of production affecting them, such as: labour, capital, land, and enterprise, inflation, economic growth, and public policies that impact these elements. It also seeks to analyse and describe the global economy. (Full article...)
Selected general articles
-
Image 1
Jan Tinbergen (/ˈtɪnbɜːrɡən/ TIN-bur-gən, Dutch: [jɑn ˈtɪmbɛrɣə(n)]; 12 April 1903 – 9 June 1994) was a Dutch economist who was awarded the first Nobel Memorial Prize in Economic Sciences in 1969, which he shared with Ragnar Frisch for having developed and applied dynamic models for the analysis of economic processes. He is widely considered to be one of the most influential economists of the 20th century and one of the founding fathers of econometrics.
His important contributions to econometrics include the development of the first macroeconometric models, the solution of the identification problem, and the understanding of dynamic models. Tinbergen was a founding trustee of Economists for Peace and Security. In 1945, he founded the Bureau for Economic Policy Analysis (CPB) and was the agency's first director. (Full article...) -
Image 2
Murray Newton Rothbard (/ˈrɒθbɑːrd/; March 2, 1926 – January 7, 1995) was an American economist of the Austrian School, economic historian, political theorist, and activist. Rothbard was a central figure in the 20th-century American libertarian movement, particularly its right-wing strands, and was a founder and leading theoretician of anarcho-capitalism (as termed by Rothbard; but later opposing the 'anarchism' label on both etymological and historical grounds). He wrote over twenty books on political theory, history, economics, and other subjects.
Rothbard argued that all services provided by the "monopoly system of the corporate state" could be provided more efficiently by the private sector and wrote that the state is "the organization of robbery systematized and writ large". He called fractional-reserve banking a form of fraud and opposed central banking. He categorically opposed all military, political, and economic interventionism in the affairs of other nations. (Full article...) -
Image 3Lithography of List by Josef Kriehuber, 1845
Daniel Friedrich List (6 August 1789 – 30 November 1846) was a German entrepreneur, diplomat, economist and political theorist who developed the nationalist theory of political economy in both Europe and the United States. He was a forefather of the German historical school of economics and argued for the Zollverein (a pan-German customs union) from a nationalist standpoint. He advocated raising tariffs on imported goods while supporting free trade of domestic goods and stated the cost of a tariff should be seen as an investment in a nation's future productivity. His theories and writing also influenced the American school of economics.
List was a political liberal who collaborated with Karl von Rotteck and Carl Theodor Welcker on the Rotteck-Welckersches Staatslexikon [de], an encyclopedia of political science that advocated constitutional liberalism and which influenced the Vormärz. At the time in Europe, liberal and nationalist ideas were almost inseparably linked, and political liberalism was not yet attached to what was later considered "economic liberalism." Emmanuel Todd considers List a forerunner to John Maynard Keynes as a theorist of "moderate or regulated capitalism." (Full article...) -
Image 4The attention economy refers to the incentives of advertising-driven companies, in particular, to maximize the time and attention their users give to their product.
Attention economics is an approach to the management of information that treats human attention as a scarce commodity and applies economic theory to solve various information management problems. (Full article...) -
Image 5Pierre Samuel du Pont de Nemours, a prominent physiocrat. In his book La Physiocratie, du Pont advocated low tariffs and free trade.
Physiocracy (French: physiocratie; from the Greek for "government of nature") is an economic theory developed by a group of 18th-century Age of Enlightenment French economists. They believed that the wealth of nations derived solely from the value of "land agriculture" or "land development" and that agricultural products should be highly priced. Their theories originated in France and were most popular during the second half of the 18th century. Physiocracy became one of the first well-developed theories of economics.
François Quesnay (1694–1774), the marquis de Mirabeau (1715–1789) and Anne-Robert-Jacques Turgot (1727–1781) dominated the movement, which immediately preceded the first modern school, classical economics, which began with the publication of Adam Smith's The Wealth of Nations in 1776. (Full article...) -
Image 6

Antoine Augustin Cournot (French: [ɑ̃twan oɡystɛ̃ kuʁno]; 28 August 1801 – 31 March 1877) was a French philosopher and mathematician who contributed to the development of economics. (Full article...) -
Image 7Critique of political economy or simply the first critique of economy is a form of social critique that rejects the conventional ways of distributing resources. The critique also rejects what its advocates believe are unrealistic axioms, flawed historical assumptions, and taking conventional economic mechanisms as a given
or as transhistorical (true for all human societies for all time). The critique asserts the conventional economy is merely one of many types of historically specific ways to distribute resources, which emerged along with modernity (post-Renaissance Western society).
Critics of political economy do not necessarily aim to create their own theories regarding how to administer economies. Critics of economy commonly view "the economy" as a bundle of concepts and societal and normative practices, rather than being the result of any self-evident economic laws. Hence, they also tend to consider the views which are commonplace within the field of economics as faulty, or simply as pseudoscience. (Full article...) -
Image 8

Piero Sraffa FBA (5 August 1898 – 3 September 1983) was an influential Italian political economist who served as lecturer of economics at the University of Cambridge. His book Production of Commodities by Means of Commodities is taken as founding the neo-Ricardian school of economics. (Full article...) -
Image 9Classical economics, also known as the classical school of economics, or classical political economy, is a school of thought in political economy that flourished, primarily in Britain, in the late 18th and early-to-mid 19th century. It includes both the Smithian and Ricardian schools. Its main thinkers are held to be Adam Smith, Jean-Baptiste Say, David Ricardo, Thomas Robert Malthus, and John Stuart Mill. These economists produced a theory of market economies as largely self-regulating systems, governed by natural laws of production and exchange (famously captured by Adam Smith's metaphor of the invisible hand).
Adam Smith's The Wealth of Nations in 1776 is usually considered to mark the beginning of classical economics. The fundamental message in Smith's book was that the wealth of any nation was determined not by the gold in the monarch's coffers, but by its national income. This income was in turn based on the labor of its inhabitants, organized efficiently by the division of labour and the use of accumulated capital, which became one of classical economics' central concepts. (Full article...) -
Image 10

Arthur Cecil Pigou (/ˈpiːɡuː/; 18 November 1877 – 7 March 1959) was an English economist. As a teacher and builder of the School of Economics at the University of Cambridge, he trained and influenced many Cambridge economists who went on to take chairs of economics around the world. His work covered various fields of economics, particularly welfare economics, but also included business cycle theory, unemployment, public finance, index numbers, and measurement of national output. His reputation was affected adversely by influential economic writers who used his work as the basis on which to define their own opposing views. He reluctantly served on several public committees, including the Cunliffe Committee and the 1919 Royal Commission on income tax. (Full article...) -
Image 11
John Maynard Keynes, 1st Baron Keynes CB, FBA (/keɪnz/ KAYNZ; 5 June 1883 – 21 April 1946), was an English economist and philosopher whose ideas fundamentally changed the theory and practice of macroeconomics and the economic policies of governments. Originally trained in mathematics, he built on and greatly refined earlier work on the causes of business cycles. One of the most influential economists of the 20th century, he produced writings that are the basis for the school of thought known as Keynesian economics, and its various offshoots. His ideas, reformulated as New Keynesianism, are fundamental to mainstream macroeconomics. He is known as the "father of macroeconomics".
During the Great Depression of the 1930s, Keynes spearheaded a revolution in economic thinking, challenging the ideas of neoclassical economics that held that free markets would, in the short to medium term, automatically provide full employment, as long as workers were flexible in their wage demands. He argued that aggregate demand (total spending in the economy) determined the overall level of economic activity, and that inadequate aggregate demand could lead to prolonged periods of high unemployment, and since wages and labour costs are rigid downwards the economy will not automatically rebound to full employment. Keynes advocated the use of fiscal and monetary policies to mitigate the adverse effects of economic recessions and depressions. After the 1929 crisis, Keynes also turned away from a fundamental pillar of neoclassical economics: free trade. He criticized Ricardian comparative advantage theory (the foundation of free trade), considering the theory's initial assumptions unrealistic, and became definitively protectionist. He detailed these ideas in his magnum opus, The General Theory of Employment, Interest and Money, published in early 1936. By the late 1930s, leading Western economies had begun adopting Keynes's policy recommendations. Almost all capitalist governments had done so by the end of the two decades following Keynes's death in 1946. As a leader of the British delegation, Keynes participated in the design of the international economic institutions established after the end of World War II but was overruled by the American delegation on several aspects. (Full article...) -
Image 12

Ludwig Heinrich Edler von Mises (/vɒn ˈmiːzɪz/; German: [ˈluːtvɪç fɔn ˈmiːzəs]; September 29, 1881 – October 10, 1973) was an Austrian-American political economist and philosopher of the Austrian school. Mises wrote and lectured extensively on the social contributions of classical liberalism and the central role of consumers in a market economy. He is best known for his work in praxeology, particularly for studies comparing communism and capitalism, as well as for being a defender of classical liberalism in the face of rising illiberalism and authoritarianism throughout much of Europe during the 20th century.
In 1940, Mises emigrated from Austria to the United States to escape the Nazis. On the day German forces entered Vienna, they raided his apartment, confiscating his papers and library, which were believed lost or destroyed until rediscovered decades later in Soviet archives. At the time, Mises was living in Geneva, Switzerland. However, with the imminent Nazi occupation of France threatening to isolate Switzerland within Axis-controlled territory, he and his wife fled through France—avoiding German patrols—and reached the United States via Spain and Portugal. (Full article...) -
Image 13Ernst Friedrich Schumacher CBE (16 August 1911 – 4 September 1977) was a German-born British statistician and economist who is best known for his proposals for human-scale, decentralised and appropriate technologies. He served as Chief Economic Advisor to the British National Coal Board from 1950 to 1970, and founded the Intermediate Technology Development Group (now known as Practical Action) in 1966.
In 1995, his 1973 book Small Is Beautiful: A Study of Economics As If People Mattered was ranked by The Times Literary Supplement as one of the 100 most influential books published since World War II. In 1977 he published A Guide for the Perplexed as a critique of materialistic scientism and as an exploration of the nature and organisation of knowledge. (Full article...) -
Image 14Mainstream economics is the body of knowledge, theories, and models of economics, as taught by universities worldwide, that are generally accepted by economists as a basis for discussion. Also known as orthodox economics, it can be contrasted to heterodox economics, which encompasses various schools or approaches that are only accepted by a small minority of economists.
The economics profession has traditionally been associated with neoclassical economics. However, this association has been challenged by prominent historians of economic thought including David Colander. They argue the current economic mainstream theories, such as game theory, behavioral economics, industrial organization, information economics, and the like, share very little common ground with the initial axioms of neoclassical economics. (Full article...) -
Image 15
Elinor Claire "Lin" Ostrom (née Awan; August 7, 1933 – June 12, 2012) was an American political scientist and political economist whose work was associated with New Institutional Economics and the resurgence of political economy. In 2009, she was awarded the Nobel Memorial Prize in Economic Sciences for her "analysis of economic governance, especially the commons", which she shared with Oliver E. Williamson; she was the first woman to win the prize.
Trained in political science at UCLA, Ostrom was a faculty member at Indiana University Bloomington for 47 years. Beginning in the 1960s, Ostrom was involved in resource management policy and created a research center, the Workshop in Political Theory and Policy Analysis, which attracted scientists from different disciplines from around the world. Working and teaching at her center was created on the principle of a workshop, rather than a university with lectures and a strict hierarchy. Late in her career, she held an affiliation with Arizona State University. (Full article...) -
Image 16
Hans-Hermann Hoppe (/ˈhɒpə/; German: [ˈhɔpə]; born 2 September 1949) is a German-American academic associated with Austrian School economics, anarcho-capitalism, right-wing libertarianism, and opposition to democracy. He is professor emeritus of economics at the University of Nevada, Las Vegas (UNLV), senior fellow of the Mises Institute think tank, and the founder and president of the Property and Freedom Society.
Hoppe has written extensively in opposition to democracy, notably in his 2001 book Democracy: The God That Failed. The book favors exclusionary "covenant communities" that are "founded for the purpose of protecting family and kin". A section of the book favoring exclusion of democrats and homosexuals from society helped popularize Hoppe on the far-right. (Full article...) -
Image 17
Alfred Marshall FBA (26 July 1842 – 13 July 1924) was an English economist and one of the most influential economists of his time. His book Principles of Economics (1890) was the dominant economic textbook in England for many years, and brought the ideas of supply and demand, marginal utility, and costs of production into a coherent whole, popularizing the modern neoclassical approach which dominates microeconomics to this day. As a result, he is known as the father of scientific economics. (Full article...) -
Image 18The Austrian school is a heterodox school of economic thought that advocates strict adherence to methodological individualism, the concept that social phenomena result primarily from the motivations and actions of individuals along with their self-interest. Austrian-school theorists hold that economic theory should be exclusively derived from basic principles of human action.
The Austrian school originated in 1871 in Vienna with the work of Carl Menger, Eugen von Böhm-Bawerk, Friedrich von Wieser, and others. It was methodologically opposed to the Historical school, in a dispute known as Methodenstreit, or methodology quarrel. Current-day economists working in this tradition are located in many countries, but their work is still referred to as Austrian economics. Among the theoretical contributions of the early years of the Austrian school are the subjective theory of value, marginalism in price theory and the formulation of the economic calculation problem. (Full article...) -
Image 19
Richard H. Thaler (/ˈθeɪlər/; born September 12, 1945) is an American economist and the Charles R. Walgreen Distinguished Service Professor of Behavioral Science and Economics at the University of Chicago Booth School of Business. In 2015, Thaler was president of the American Economic Association.
Thaler is a theorist in behavioral economics. He has collaborated with Daniel Kahneman, Amos Tversky, and others in further defining that field. In 2018, he was elected a member in the National Academy of Sciences. (Full article...) -
Image 20
Oskar Ryszard Lange (Polish: [ˈlanɡɛ]; 27 July 1904 – 2 October 1965) was a Polish economist and diplomat. He is best known for advocating the use of market pricing tools in socialist systems and providing a model of market socialism. He responded to the economic calculation problem proposed by Ludwig von Mises and Friedrich Hayek by claiming that managers in a centrally-planned economy would be able to monitor supply and demand through increases and declines in inventories of goods, and advocated the nationalization of major industries. During his stay in the United States, Lange was an academic teacher and researcher in mathematical economics. Later in socialist Poland, he was a member of the Central Committee of the Polish United Workers' Party. (Full article...) -
Image 21Humanistic economics is a distinct pattern of economic thought with old historical roots that have been more recently invigorated by E. F. Schumacher's Small Is Beautiful: Economics as if People Mattered (1973). Proponents argue for "persons-first" economic theories as opposed to mainstream economic theories which are understood as often emphasizing financial gain over human well-being. In particular, the overly abstract human image implicit in mainstream economics is critically analyzed and instead it attempts a rethinking of economic principles, policies and institutions based on a richer and more balanced view of human nature. (Full article...)
-
Image 22
François Quesnay (/keɪˈneɪ/; French: [fʁɑ̃swa kɛnɛ]; 4 June 1694 – 16 December 1774) was a French economist and physician of the Physiocratic school. He is known for publishing the "Tableau économique" (Economic Table) in 1758, which provided the foundations of the ideas of the Physiocrats. This was perhaps the first work attempting to describe the workings of the economy in an analytical way, and as such can be viewed as one of the first important contributions to economic thought. His Le Despotisme de la Chine, written in 1767, describes Chinese politics and society, and his own political support for enlightened despotism. (Full article...) -
Image 23

Seaport at sunset, a painting by Claude Lorrain, completed in 1639 at the height of mercantilism
Mercantilism is a nationalist economic policy that is designed to maximize the exports and minimize the imports of an economy. It seeks to maximize the accumulation of resources within the country and use those resources for one-sided trade.
The concept aims to reduce a possible current account deficit or reach a current account surplus, and it includes measures aimed at accumulating monetary reserves by a positive balance of trade, especially of finished goods. Historically, such policies may have contributed to war and motivated colonial expansion. Mercantilist theory varies in sophistication from one writer to another and has evolved over time. (Full article...) -
Image 24
Tjalling Charles Koopmans (August 28, 1910 – February 26, 1985) was a Dutch-American mathematician and economist. He was the joint winner with Leonid Kantorovich of the 1975 Nobel Memorial Prize in Economic Sciences for his work on the theory of the optimum allocation of resources. Koopmans showed that on the basis of certain efficiency criteria, it is possible to make important deductions concerning optimum price systems. (Full article...) -
Image 25Computational economics is an interdisciplinary research discipline that combines methods in computational science and economics to solve complex economic problems. This subject encompasses computational modeling of economic systems. Some of these areas are unique, while others established areas of economics by allowing robust data analytics and solutions of problems that would be arduous to research without computers and associated numerical methods.
Computational methods have been applied in various fields of economics research, including but not limiting to: (Full article...)
Did you know...
- ... that environmental economist V. Kerry Smith has been described as a "Renaissance Man of Economics"?
- ... that a banker was named the prime minister of Equatorial Guinea after his predecessor resigned during an economic crisis?
- ... that the Canadian journalist Bernard Descôteaux is credited with the economic revival of the independent newspaper Le Devoir?
- ... that Ruth Huenemann was one of the first researchers to make a connection between socioeconomic status and childhood obesity?
- ... that soprano Galina Pisarenko studied economics, English, and Norwegian at the same time she was studying to become a professional opera singer?
- ... that Michael Kremer's O-ring theory of economic development was inspired by his forgetting to purchase toilet paper for a training session?
Need help?
Do you have a question about Economics that you can't find the answer to?
Consider asking it at the Wikipedia reference desk.
Get involved
For editor resources and to collaborate with other editors on improving Wikipedia's Economics-related articles, see WikiProject Economics.
Selected images
-
Image 1The publication of Adam Smith's The Wealth of Nations in 1776 is considered to be the first formalisation of economic thought.
-
Image 3São Paulo Stock Exchange in Brazil, an electronic trading network that brings together buyers and sellers through an electronic trading platform
-
Image 4A 1638 painting of a French seaport during the heyday of mercantilism
-
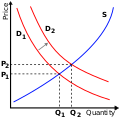
Image 5The supply and demand model describes how prices vary as a result of a balance between product availability and demand. The graph depicts an increase in demand from D1 to D2 and the resulting increase in price and quantity required to reach a new equilibrium point on the supply curve (S).
-
Image 6Economists study trade, production, and consumption decisions, including those that occur in a traditional marketplace
-
Image 12Pollution can be a simple example of market failure; if costs of production are not borne by producers but are by the environment, accident victims or others, then prices are distorted.
-
Image 13The Marxist critique of political economy comes from the work of German philosopher Karl Marx.
-
Image 14An environmental scientist sampling water
In the news
- 30 June 2025 – 2025 United States trade war with Canada and Mexico
- White House economic advisor Kevin Hassett announces that the United States will restart trade talks with Canada after they have scrapped their digital services tax on American technology firms. (CBC)
Subcategories
Subtopics
Associated Wikimedia
The following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
-
Commons
Free media repository -
Wikibooks
Free textbooks and manuals -
Wikidata
Free knowledge base -
Wikinews
Free-content news -
Wikiquote
Collection of quotations -
Wikisource
Free-content library -
Wikiversity
Free learning tools -
Wiktionary
Dictionary and thesaurus
- Pages with Dutch IPA
- Pages with French IPA
- Pages with German IPA
- Pages with Polish IPA
- Single-page portals
- Portals with no named maintainer
- Automated article-slideshow portals with article list built solely from one template
- Automated article-slideshow portals with 101–200 articles in article list
- Portals needing placement of incoming links

![Image 1 Tinbergen in 1982 Jan Tinbergen (/ˈtɪnbɜːrɡən/ TIN-bur-gən, Dutch: [jɑn ˈtɪmbɛrɣə(n)]; 12 April 1903 – 9 June 1994) was a Dutch economist who was awarded the first Nobel Memorial Prize in Economic Sciences in 1969, which he shared with Ragnar Frisch for having developed and applied dynamic models for the analysis of economic processes. He is widely considered to be one of the most influential economists of the 20th century and one of the founding fathers of econometrics. His important contributions to econometrics include the development of the first macroeconometric models, the solution of the identification problem, and the understanding of dynamic models. Tinbergen was a founding trustee of Economists for Peace and Security. In 1945, he founded the Bureau for Economic Policy Analysis (CPB) and was the agency's first director. (Full article...)](http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/en/d/d2/Blank.png)