Portal:Ecology/Selected picture
Appearance
Selected picture 1
Portal:Ecology/Selected picture/1

Credit: Luc Viatour
Grasslands are found in most ecoregions of the Earth. Above are grasslands near Elsrickle, South Lanarkshire, Great Britain.
Selected picture 2
Portal:Ecology/Selected picture/2
Wasp mimicry - A and B show real wasps; the rest are mimics: three hoverflies and one beetle. Mimicry is part of the evolutionary process of adaptation.
Selected picture 3
Portal:Ecology/Selected picture/3
Topsoil is the upper, outermost layer of soil, usually the top 2 inches (5.1 cm) to 8 inches (20 cm). It has the highest concentration of organic matter and microorganisms and is where most of the Earth's biological soil activity occurs. Pictured: Terraces, conservation tillage, and conservation buffers save soil, control erosion and improve water quality on this Iowa farm. 1999.
Selected picture 4
Portal:Ecology/Selected picture/4

Credit: Mnolf
A Venus Flytrap (Dionaea muscipula) closing after receiving a stimulus. Venus Flytraps are carnivorous plants that catch and digest animal prey—mostly insects and arachnids.
Selected picture 5
Portal:Ecology/Selected picture/5

Credit: Composite image created by User:Medeis
Selected picture 6
Portal:Ecology/Selected picture/6
Drawing of an American paddlefish (Polyodon spathula). Also called the Mississippi paddlefish or spoonbill, they live in slow-flowing waters of the Mississippi River drainage system and may grow to 7 feet (220 cm) and weigh up to 220 pounds (100 kg). They appear to have been extirpated from Lake Erie and its tributaries.
Selected picture 7
Portal:Ecology/Selected picture/7
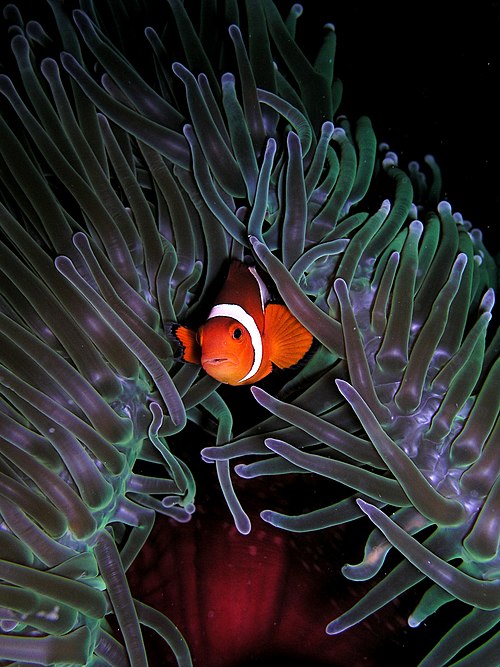

Credit: User:Nhobgood
Ocellaris clownfish often live symbiotically with the Heteractis magnifica sea anemone, using them for shelter and protection.
Selected picture 8
Portal:Ecology/Selected picture/8
Some Hydrothermal vents support peculiar ecosystems, based on dissolved minerals. Hydrothermal vent communities are able to sustain such vast amounts of life because vent organisms depend on chemosynthetic bacteria for food. The water that comes out of the hydrothermal vent is rich in dissolved minerals and supports a large population of chemo-autotrophic bacteria.
Selected picture 9
Portal:Ecology/Selected picture/9
Credit: Nicolas Pourcelot
A limule (Horseshoe crab) in the Hạ Long Bay, Quảng Ninh province, Vietnam. Horseshoe crabs are arthropods that live primarily in shallow ocean waters on soft sandy or muddy bottoms.
Selected picture 10
Portal:Ecology/Selected picture/10

Credit: Andrew Dunn (User:Solipsist)
Selected picture 11
Portal:Ecology/Selected picture/11

Credit: U.S. Navy
Three polar bears approach the USS Honolulu (SSN-718), 280 miles from the North Pole. Polar bears have adapted through the process of evolution to have white fur that matches the white, icy arctic tundra.
Selected picture 12
Selected picture 13
Portal:Ecology/Selected picture/13

Credit: Paul Lenz
Selected picture 14
Portal:Ecology/Selected picture/14
Sunflowers were domesticated by humans, and are native to Central America. The evidence thus far is that it was first domesticated in Mesoamerica|, present day Mexico, by at least 2600 BC. It may have been domesticated a second time in the middle Mississippi Valley, or been introduced there from Mexico at an early date, as maize was. Sunflower leaves can be used as a cattle feed, while the stems contain a fiber which may be used in paper production.
Selected picture 15
Portal:Ecology/Selected picture/15
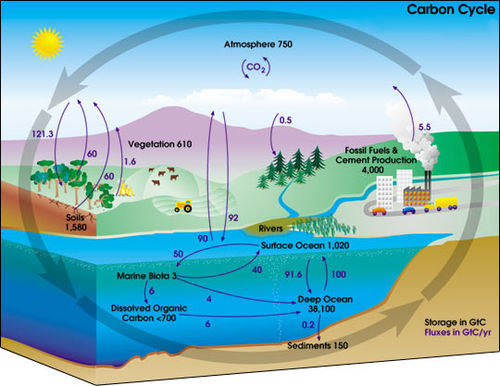
Credit: NASA
The carbon cycle is the biogeochemical cycle by which carbon is exchanged between the biosphere, geosphere, hydrosphere, and atmosphere of the Earth. Burning fossil fuels leads to the addition of extra carbon into the cycle over what naturally occurs and is a major cause of climate change.
Selected picture 16
Portal:Ecology/Selected picture/16
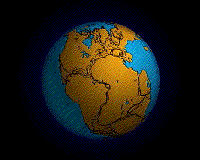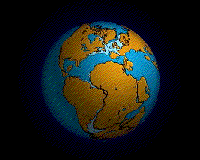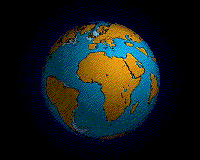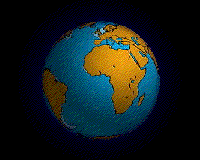
An animation of the Earth's hypothesized Pangaea separation. Pangaea is hypothesized as a supercontinent that existed during the Paleozoic and Mesozoic eras about 250 million years ago, before the component continents were separated into their current configuration.
Selected picture 17
Portal:Ecology/Selected picture/17
Lightning is an atmospheric electrostatic discharge (spark) accompanied by thunder, which typically occurs during thunderstorms, and sometimes during volcanic eruptions or dust storms. The study of the atmosphere and atmospheric variables that affect various ecoregions and ecosystems is a significant part of the discipline of Ecology.
Selected picture 18
Selected picture 19
Portal:Ecology/Selected picture/19

Credit: User:God of War
A rocky stream in Hawaii, an example of a riparian zone. A riparian zone or riparian area is the interface between land and a river or stream.
Selected picture 20
Portal:Ecology/Selected picture/20
An area of the Amazon Rainforest in Brazil. The tropical rainforests of South America contain the largest diversity of species on Earth.
Selected picture 21
Portal:Ecology/Selected picture/21
Schooling bigeye trevally. In biology, any group of fish that stay together for social reasons are said to be shoaling and if the group is swimming in the same direction in a coordinated manner, they are said to be schooling.
Selected picture 22
Portal:Ecology/Selected picture/22

Credit: Martin St-Amant
The Iguazu Falls, on the border of Brazil and Argentina are waterfalls of the Iguazu River located on the border of the Brazilian State of Paraná and the Argentine Province of Misiones.
Selected picture 23
Portal:Ecology/Selected picture/23

Credit: User:Fir0002
A bee swarm of Apis mellifera ligustica (the Italian bee), a sub-species of the western honey bee (Apis mellifera), on a fallen log
Selected picture 24